Cat. #154813
Anti-CD45RB [PD7/26] rAb
Cat. #: 154813
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 10-12 weeks
Target: Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C (PTPRC, CD45RB)
Class: Recombinant
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Institute: Absolute Antibody ; University of Oxford
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Name: Anti-CD45RB [PD7/26] rAb
- Alternate name: Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase; Receptor Type C; CD45 Antigen; CD45; L-CA; T2; Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase; Receptor Type; C Polypeptide; T2 Leukocyte Common Antigen; T2 Glycoprotein; EC 3.1.3.48; GP18; CD45R; B22; LCA; LY5
- Clone: PD7/26
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Recombinant
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
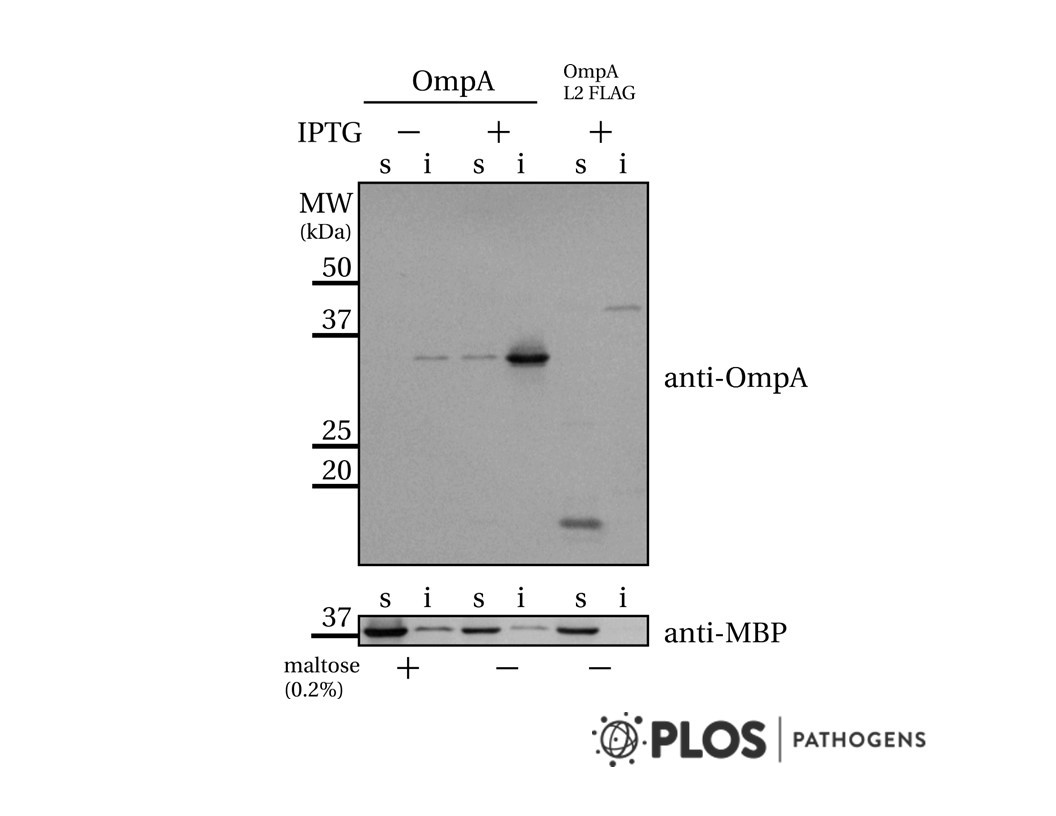
- Description: Recombinant monoclonal antibody capable of detecting CD45RB in paraffin-embedded samples, and aids in differentiating between lymphoid and non-lymphoid tumours of B-cell origin. Background and Research Application CD45RB is a protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor that is present on most hematopoietic cells and absent on non-hematopoietic cells. It is a transmembrane pan-leukocyte protein with tyrosine phosphatase activity and is involved in the regulation of signal transduction in haematopoiesis and the threshold of T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signalling. This is via dephosphorylation of protein tyrosine kinases (e.g. Lck and Fyn). Expression of CD45RB is more limited than CD45 and can only be found on T cell subsets, B, NK, and myeloid cells. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been shown to express low levels of CD45RB, linked to increased migration to sites of infection. CD45RB is expressed on the majority of lymphomas and leukaemiaĂÂs of B-cell origin. Anti-CD45RB is useful in differentiating between lymphoid and non-lymphoid tumours. CD45 regulates Src-family kinases, integrin-mediated signal transduction pathways and can suppress JAK kinases, acting as a negative regulator of cytokine receptor signalling. All CD45 isoforms share the same transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains, however their extracellular domains vary, depending on the spliced product. Recombinant anti-CD45RB is capable of recognising antigens in fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues, unlike other reagents of similar specificity. It is the recombinant version of anti-CD45RB. This antibody reacts with an epitope which does not become denatured or masked during fixation and embedding.
- Immunogen: Human PBL maintained in T-cell growth factor
- Immunogen uniprot id: P08575
- Isotype: IgG1
Target Details
- Target: Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C (PTPRC, CD45RB)
- Target background: Recombinant monoclonal antibody capable of detecting CD45RB in paraffin-embedded samples, and aids in differentiating between lymphoid and non-lymphoid tumours of B-cell origin. Background and Research Application CD45RB is a protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor that is present on most hematopoietic cells and absent on non-hematopoietic cells. It is a transmembrane pan-leukocyte protein with tyrosine phosphatase activity and is involved in the regulation of signal transduction in haematopoiesis and the threshold of T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signalling. This is via dephosphorylation of protein tyrosine kinases (e.g. Lck and Fyn). Expression of CD45RB is more limited than CD45 and can only be found on T cell subsets, B, NK, and myeloid cells. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been shown to express low levels of CD45RB, linked to increased migration to sites of infection. CD45RB is expressed on the majority of lymphomas and leukaemia's of B-cell origin. Anti-CD45RB is useful in differentiating between lymphoid and non-lymphoid tumours. CD45 regulates Src-family kinases, integrin-mediated signal transduction pathways and can suppress JAK kinases, acting as a negative regulator of cytokine receptor signalling. All CD45 isoforms share the same transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains, however their extracellular domains vary, depending on the spliced product. Recombinant anti-CD45RB is capable of recognising antigens in fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues, unlike other reagents of similar specificity. It is the recombinant version of anti-CD45RB. This antibody reacts with an epitope which does not become denatured or masked during fixation and embedding.
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Concentration: 1 mg/ml
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage conditions: Store at -20° C frozen. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles
- Shipping conditions: Shipping at 4° C
References
- A hydrogel-endothelial cell implant mimics infantile hemangioma: modulation by survivin and the Hippo pathway.
- Brand et al. 2015. J Biol Chem. :. PMID: 25918170.
- Chijiwa et al. 2015. Int J Oncol. :. PMID: 25963555.
- Diagnosis of human lymphoma with monoclonal antileukocyte antibodies.
- Establishment of patient-derived cancer xenografts in immunodeficient NOG mice.
- Gatter et al. 1983. J Biol Response Mod. 2(4):369-95. PMID: 6196454.
- Histiocytic Sarcoma Originating in the Lung in a 16-Year-Old Male.
- Lapa et al. 2015. PLoS One. 10(3):e0122269. PMID: 25807228.
- Monoclonal antibodies in diagnostic pathology: techniques and applications.
- Preza et al. 2015. PLoS One. 10(4):e0122723. PMID: 25856343.
- T lymphocyte density and distribution in human colorectal mucosa, and inefficiency of current cell isolation protocols.
- Tomita et al. 2015. J Clin Exp Hematop. 55(1):45-9. PMID: 26106007.
- Transforming Growth Factor-? and Interleukin-1? Signaling Pathways Converge on the Chemokine CCL20 Promoter.
- Tsuneki et al. 2015. Lab Invest. :. PMID: 25961170.
- Tumor-associated macrophages in glioblastoma multiforme-a suitable target for somatostatin receptor-based imaging and therapy?
- Warnke et al. 1983. N Engl J Med. 309(21):1275-81. PMID: 6355845.