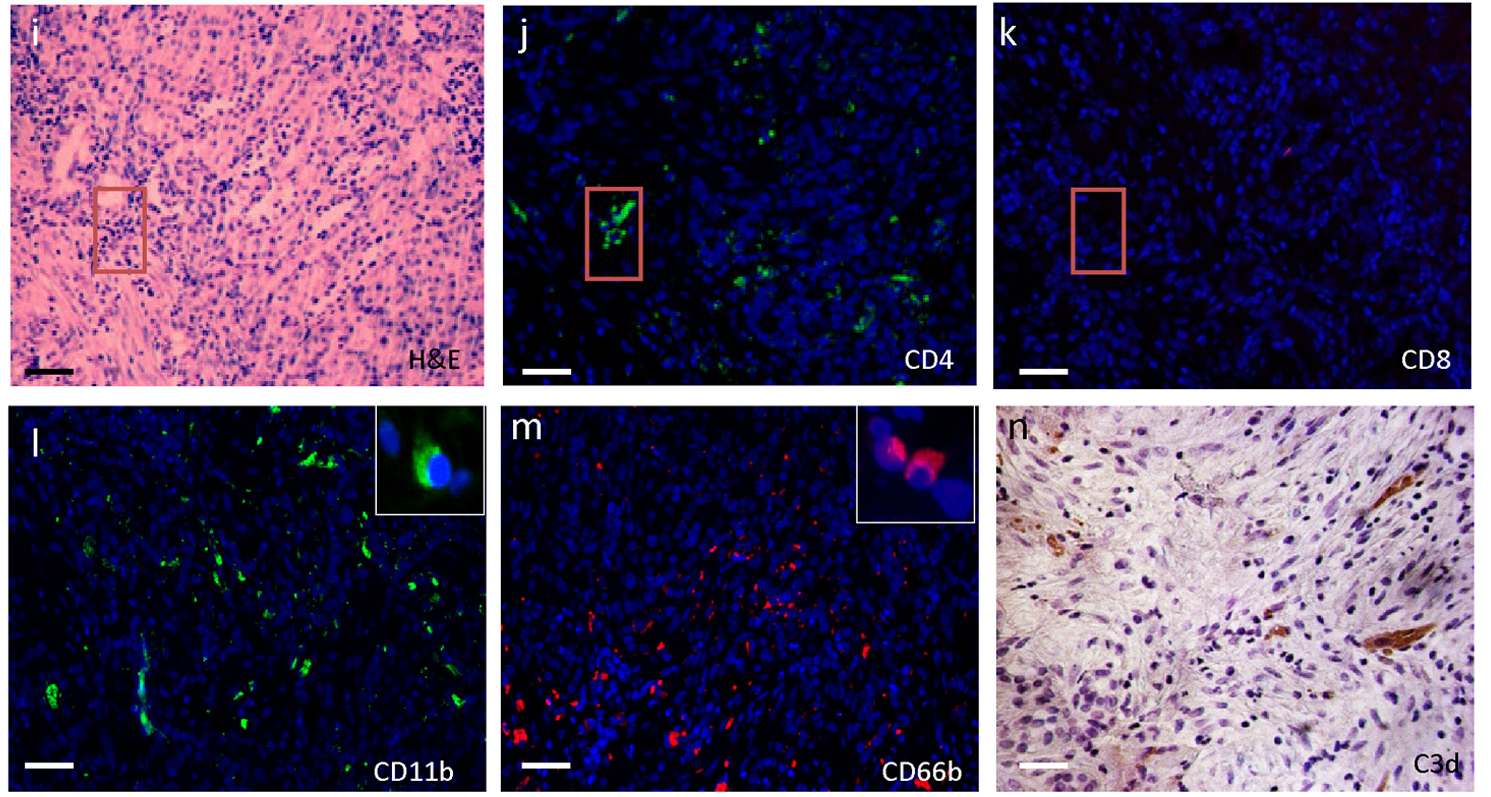
Cat. #153997
MMTV TET-LRH-1 Transgenic Mouse
Cat. #: 153997
Sub-type: Mouse
Availability: 6-8 weeks
Disease: Cancer; Pregnancy; Inflammatory bowel disease; Lipid metabolism; Steriodogenesis
Model: Transgenic
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Colin Clyne
Institute: Hudson Institute of Medical Research
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Tool name: MMTV TET-LRH-1 Transgenic Mouse
- Alternate name: LRH-1
- Tool sub type: Mouse
- Disease: Cancer; Pregnancy; Inflammatory bowel disease; Lipid metabolism; Steriodogenesis
- Model: Transgenic
- Conditional: Yes
- Conditional description: It conditionally expresses LRH-1 (and a DsRed fluorescent marker) from a tetracycline-responsive promoter when crossed with a line that expresses the reverse tetracycline-dependent transactivator (rtTA, or âTet-onâ) and is given doxycycline, which activates the LRH-1 / DsRed expression.
- Description: Mouse has no phenotype; when crossed with an appropriate tissuse-specific rtTA line, doxycycline administration to the double transgenic line will induce LRH-1 and DsRed expression in the tissue of interest. Induces key genes to regulate metabolic process, ovarian function, cancer cell proliferation, and steroidogenesis. In the breast, LRH-1 modulates and synergizes with endogenous estrogen signaling to promote breast cancer cell proliferation.
- Genetic background: The pTetOLRH-1transgene was generated from a construct containing the human LRH-1 open reading frame. A Kozak sequence was introduced by site-directed mutagenesis using the QuikChange II Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Agilent Technologies) and primers F-Kozak (5-TTAAGCCAAAGAACTGCCTATAATTTCACTCACCATGGCTTCTAATTCAGATACTGGGGATTTACAAG-3) and R-Kozak (5-CTTGTAAATCCCCAGTATCTGAATTAGAAGCCATGGTGAGTGAAATTATAGGCAGTTCTTTGGCTTAA-3). The LRH-1 open reading frame containing the Kozak sequence was then subcloned into the multiple cloning site of the pTRE-Tight-BI-DsRed Express vector (Clontech) after NotI restriction digest. Orientation of the insert was verified by digesting the vector with BamHI. The vector was then linearized using ApaLI and gel purified. The pTetOLRH-1 founder mice were generated by pronuclear injection (MouseWorksService) of the purified transgene, and complete transgene insertion was verified using primers that spanned the 3_ end of the DsRed open reading frame (L1) (forward 5-GCCGATGAACTTCACCTTGT-3 and reverse 5-CGAGGACGTCATCAAGGAGT-3_) and the 3_ end of the LRH-1 open reading frame (L2) (forward 5_-TCGACCACATTTACCGACAA-3 and reverse 5_-TGGCTGATTATGATCCTCTGG-3). MMTVrtTA-pTetOLRH-1 (MMTVtet-LRH-1) double-transgenic mice were generated by crossing pTetOLRH-1 founder females with MMTVrtTA males. Genotyping of double-transgenic animals was performed using the primers for LRH-1 listed above and MTB forward (TGCCGCCATTATTACGACAAGC) and reverse (ACCGTACTCGTCAATTCCAAGGG).
- Phenotype: Mouse has no phenotype
- Zygosity: Homozygous
- Strain: C57BL/6
- Production details: The pTetOLRH-1transgene was generated from a construct containing the human LRH-1 open reading frame. A Kozak sequence was introduced by site-directed mutagenesis using the QuikChange II Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Agilent Technologies) and primers F-Kozak (5-TTAAGCCAAAGAACTGCCTATAATTTCACTCACCATGGCTTCTAATTCAGATACTGGGGATTTACAAG-3) and R-Kozak (5-CTTGTAAATCCCCAGTATCTGAATTAGAAGCCATGGTGAGTGAAATTATAGGCAGTTCTTTGGCTTAA-3). The LRH-1 open reading frame containing the Kozak sequence was then subcloned into the multiple cloning site of the pTRE-Tight-BI-DsRed Express vector (Clontech) after NotI restriction digest. Orientation of the insert was verified by digesting the vector with BamHI. The vector was then linearized using ApaLI and gel purified. The pTetOLRH-1 founder mice were generated by pronuclear injection (MouseWorksService) of the purified transgene, and complete transgene insertion was verified using primers that spanned the 3_ end of the DsRed open reading frame (L1) (forward 5-GCCGATGAACTTCACCTTGT-3 and reverse 5-CGAGGACGTCATCAAGGAGT-3_) and the 3_ end of the LRH-1 open reading frame (L2) (forward 5_-TCGACCACATTTACCGACAA-3 and reverse 5_-TGGCTGATTATGATCCTCTGG-3). MMTVrtTA-pTetOLRH-1 (MMTVtet-LRH-1) double-transgenic mice were generated by crossing pTetOLRH-1 founder females with MMTVrtTA males. Genotyping of double-transgenic animals was performed using the primers for LRH-1 listed above and MTB forward (TGCCGCCATTATTACGACAAGC) and reverse (ACCGTACTCGTCAATTCCAAGGG).
- Breeding information: From good breeder to exceptional breeder. It depends on the age of the mouse.
- Additional notes: Breast Cancer
- Recommended controls: No
Handling
- Shipping conditions: Embryo/Spermatoza- Dry Ice
Target Details
- Target: Liver Receptor Homolog-1
References
- Lazarus et al. 2014. Endocrinology. 155(5):1606-17. PMID: 24564400.
- Conditional overexpression of liver receptor homolog-1 in female mouse mammary epithelium results in altered mammary morphogenesis via the induction of TGF-
.