Cat. #153636
Anti-Follistatin 288 [29/9]
Cat. #: 153636
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 10-12 weeks
Target: Follistation 288
Class: Monoclonal
Application: ELISA
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Institute: BioServ UK Ltd
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Name: Anti-Follistatin 288 [29/9]
- Alternate name: Follistatin, FS, FST, Active-binding protein
- Clone: 3.22222222222
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Molecular weight: 37 kDa
- Strain: Balb/c
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
- Application: ELISA
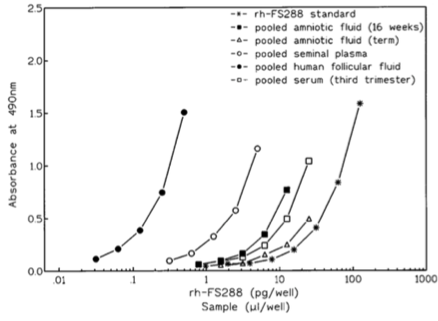
- Description: Follistatin is a single-chain glycosylated protein that inhibits follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) release. Alternative splicing of Follistatin mRNA yields two isoforms, FS315 and FS288. FS288 is the main cell-surface form and binds to surface heparin sulphate proteoglycans. 29/9 is a clone raised against recombinant Fst 288, and is used in combination, commonly as the capture, with antibody 17/2 in a two site ELISA for the detection of Follistatin.
- Immunogen: Raised to human Follistatin (Fst) 288 and recognizes both human Fst 288 and 315
- Isotype: IgG1
- Myeloma used: Sp2/0-Ag14
- Recommended controls: Testis or Ovary
Target Details
- Target: Follistation 288
- Molecular weight: 37 kDa
- Tissue cell line specificity: Testis or Ovary
- Target background: Follistatin is a single-chain glycosylated protein that inhibits follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) release. Alternative splicing of Follistatin mRNA yields two isoforms, FS315 and FS288. FS288 is the main cell-surface form and binds to surface heparin sulphate proteoglycans. 29/9 is a clone raised against recombinant Fst 288, and is used in combination, commonly as the capture, with antibody 17/2 in a two site ELISA for the detection of Follistatin.
Applications
- Application: ELISA
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Shipping conditions: Shipping at 4° C
References
- Hughes et al. 2003. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15(2):127-31. PMID: 12560755.
- Activin A and follistatin in acute liver failure.
- Yuen et al. 2002. Scand J Gastroenterol. 37(2):233-8. PMID: 11843063.
- Transforming growth factor-beta 1, activin and follistatin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and patients with alcoholic cirrhosis.
- Menon et al. 2000. BJOG. 107(9):1069-74. PMID: 11002947.
- Serum inhibin, activin and follistatin in postmenopausal women with epithelial ovarian carcinoma.
- McPherson et al. 1999. Endocrinology. 140(11):5303-9. PMID: 10537161.
- Expression of activin A and follistatin core proteins by human prostate tumor cell lines.
- Cuckle et al. 1999. Prenat Diagn. 19(6):513-6. PMID: 10416964.
- Maternal serum activin A and follistatin levels in pregnancies with Down syndrome.
- Fowler et al. 1998. Hum Reprod. 13(12):3530-6. PMID: 9886545.
- Anderson et al. 1998. Hum Reprod. 13(12):3319-25. PMID: 9886507.
- Follistatin and activin A production by the male reproductive tract.
- A longitudinal study of maternal serum inhibin-A, inhibin-B, activin-A, activin-AB, pro-alphaC and follistatin during pregnancy.
- Riley et al. 1998. Hum Reprod. 13(9):2624-8. PMID: 9806296.
- Follistatin and activin A in extra-embryonic coelomic and amniotic fluids and maternal serum in early pregnancy.
- Evans et al. 1998. J Endocrinol. 156(2):275-82. PMID: 9518873.
- Development, validation and application of an ultra-sensitive two-site enzyme immunoassay for human follistatin.
- Petraglia et al. 1997. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 82(9):2991-5. PMID: 9284732.
- Changes of dimeric inhibin B levels in maternal serum throughout healthy gestation and in women with gestational diseases.