Cat. #153202
Anti-HPV16E2 [HPV16E2]
Cat. #: 153202
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Target: HPV16E2
Class: Polyclonal
Application: IHC ; WB
Reactivity: Human
Host: Rabbit
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Institute: A*STAR Accelerate Technologies Pte Ltd
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Name: Anti-HPV16E2 [HPV16E2]
- Alternate name: Human papillomavirus type 16; Regulatory protein E2
- Clone: HPV16E2
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Polyclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Rabbit
- Application: IHC ; WB
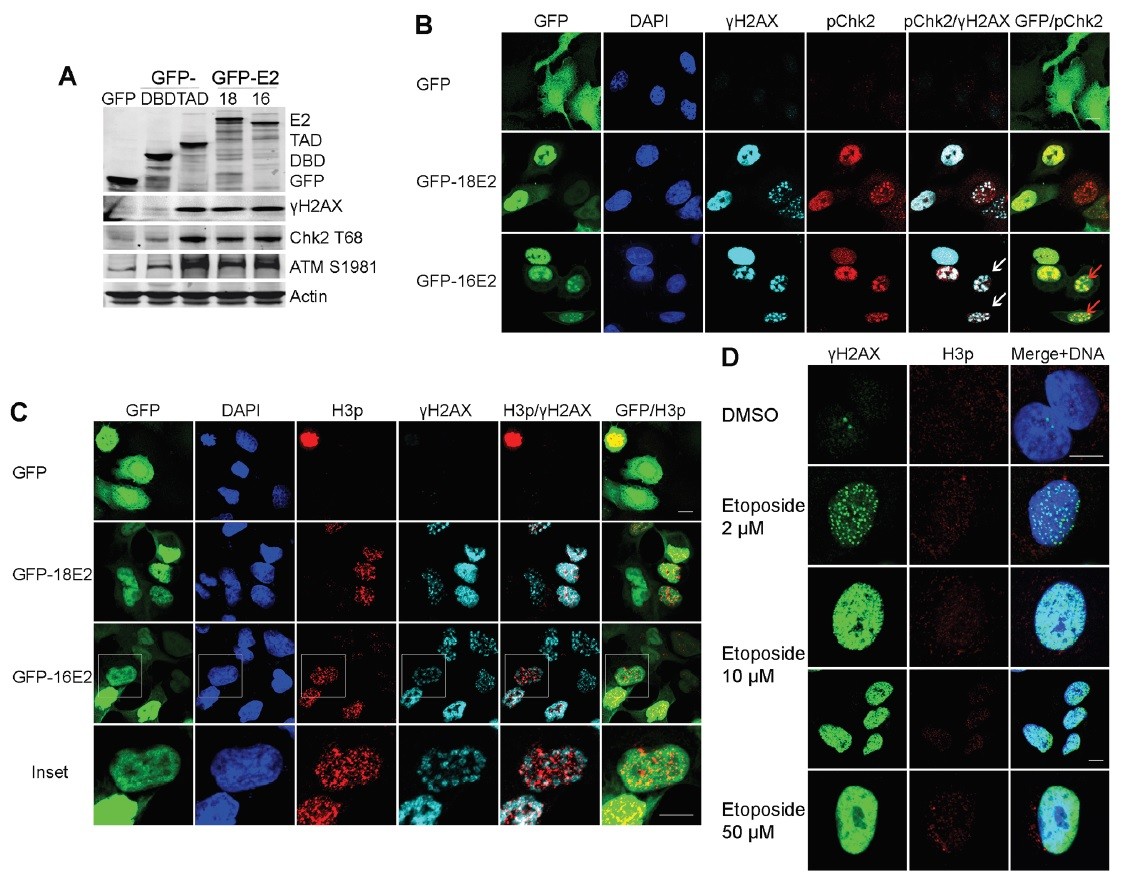
- Description: Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and is the precursor to cervical carcinoma. The completion of the HPV productive life cycle depends on the expression of viral proteins. Initiation of the viral productive replication requires expression of the E2 viral protein that cooperates with the E1 viral DNA helicase. A novel and important role for the HPV16-E2 protein in controlling host cell cycle during malignant transformation was recently revealed. Xells expressing HPV16-E2 in vitro were arrested in prophase alongside activation of a sustained DDR signal. In vivo, HPV16-E2 protein is present in cells that express both mitotic and DDR signals specifically in CIN3 lesions, immediate precursors of cancer, suggesting that E2 may be one of the drivers of genomic instability and carcinogenesis in vivo.
- Immunogen: GST-HPV16 E2 (209365)
- Immunogen uniprot id: TBC
Target Details
- Target: HPV16E2
- Target background: Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and is the precursor to cervical carcinoma. The completion of the HPV productive life cycle depends on the expression of viral proteins. Initiation of the viral productive replication requires expression of the E2 viral protein that cooperates with the E1 viral DNA helicase. A novel and important role for the HPV16-E2 protein in controlling host cell cycle during malignant transformation was recently revealed. Xells expressing HPV16-E2 in vitro were arrested in prophase alongside activation of a sustained DDR signal. In vivo, HPV16-E2 protein is present in cells that express both mitotic and DDR signals specifically in CIN3 lesions, immediate precursors of cancer, suggesting that E2 may be one of the drivers of genomic instability and carcinogenesis in vivo.
Applications
- Application: IHC ; WB
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Concentration: 0.9-1.1 mg/ml
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage buffer: Whole serum
- Storage conditions: -15° C to -25° C
- Shipping conditions: Shipping at 4° C
References
- Xue et al. 2015. Oncotarget. 6(33):34979-91. PMID: 26474276.
- HPV16-E2 induces prophase arrest and activates the cellular DNA damage response in vitro and in precursor lesions of cervical carcinoma.
- Xue et al. 2010. Cancer Res. 70(13):5316-25. PMID: 20530671.
- HPV16 E2 is an immediate early marker of viral infection, preceding E7 expression in precursor structures of cervical carcinoma.