Cat. #152051
pJEK6 Alpha-Synuclein E46K Vector
Cat. #: 152051
Availability: Please enquire for quantities and pricing
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Dr Fiona Benson
Institute: Lancaster University
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Tool name: pJEK6 Alpha-Synuclein E46K Vector
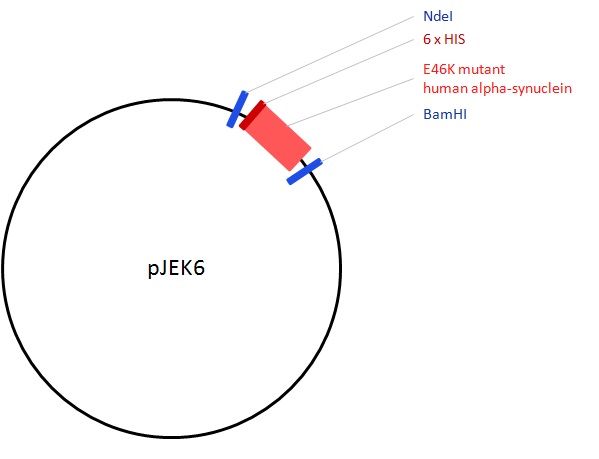
- Description: pJEK6 ("E46K") is a derivative of pET15b with the open reading frame encoding the E46K mutant human alpha synuclein (ÄÂĂÂ -synuclein) cloned in via the NdeI and BamHI restriction sites. It was constructed via site specific mutagenesis of pJEK1, replacing the G at position 136 in the ORF nucleotide sequence with A, thus altering the 46th codon from GAG encoding Glutamic Acid (E) to AAG encoding Lys (K). In this construct E46K ÄÂĂÂ -synuclein is expressed as a fusion protein with an N-terminal six His tag.
- Additional notes: Alpha synuclein is expressed predominantly in the brain, where it is concentrated in presynaptic nerve terminals. The deposition of the abundant presynaptic brain protein alpha-synuclein as fibrillary aggregates in neurons or glial cells is a hallmark lesion in a subset of neurodegenerative disorders. These disorders include Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and multiple system atrophy, collectively referred to as synucleinopathies. Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive accumulation in selected neurons of protein inclusions containing alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin. Among the familial mutations of α-synuclein in Parkinson′s disease, E46K has the greatest potential to aggregate.
Application Details
- Application notes: pJEK6 ("E46K") is a derivative of pET15b with the open reading frame encoding the E46K mutant human alpha synuclein (α-synuclein) cloned in via the NdeI and BamHI restriction sites. It was constructed via site specific mutagenesis of pJEK1, replacing the G at position 136 in the ORF nucleotide sequence with A, thus altering the 46th codon from GAG encoding Glutamic Acid (E) to AAG encoding Lys (K). In this construct E46K α-synuclein is expressed as a fusion protein with an N-terminal six His tag.