Cat. #151831
Protein Kinase D inhibitor CRT0066101 Small Molecule (Tool Compound)
Cat. #: 151831
Sub-type: Inhibitor
Availability: Please enquire for quantities and pricing
Application: In Panc-1 subcutaneous xenograft model, orally administration of CRT0066101 at the dosage of 80 mg/kg/d for 24 days significantly suppressed pancreatic cancer growth. Moreover, when CRT0066101 reached its peak concentration (12 Îźmol/L) in tumor model, the expression of activated PKD1/2 in the treated tumor explants was substantially decreased. It was concluded that CRT0066101 given orally at 80 mg/kg/d for 21 days in Panc-1 orthotropic model suppressed tumor growth potently in vivo. Clinical...
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Mark Charles
Institute: Cancer Research Technology
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Tool name: Protein Kinase D inhibitor CRT0066101 Small Molecule (Tool Compound)
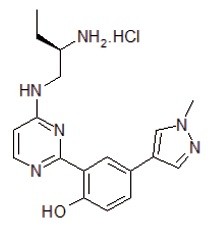
- Molecular formula: C18H23CIN6
- Tool sub type: Inhibitor
- Primary target: Protein Kinase D (PKD)
- Description: The Protein Kinase D inhibitor CRT0066101 is a potent antitumoral agent in vitro and in vivo. Protein kinase D (PKD) is an evolutionarily conserved protein kinase family with structural, enzymological, and regulatory properties different from the PKC family members. Signaling through PKD is induced by a remarkable number of stimuli, including G-protein-coupled receptor agonists and polypeptide growth factors. PKD1, the most studied member of the family, is increasingly implicated in the regu...
- Application: In Panc-1 subcutaneous xenograft model, orally administration of CRT0066101 at the dosage of 80 mg/kg/d for 24 days significantly suppressed pancreatic cancer growth. Moreover, when CRT0066101 reached its peak concentration (12 Îźmol/L) in tumor model, the expression of activated PKD1/2 in the treated tumor explants was substantially decreased. It was concluded that CRT0066101 given orally at 80 mg/kg/d for 21 days in Panc-1 orthotropic model suppressed tumor growth potently in vivo. Clinical...
- Purpose: Inhibitor
- Selectivity: Selectivity for PKD against a panel of >90 protein kinases, including PKCÎą, MEK, ERK, c-Raf and c-Src.
- Iupac: 2-[4-((R)-2-Amino-butylamino)-pyrimidin-2-yl]-4-(1-methyl-1Hpyrazol-4-yl)-phenol; hydrochloride
- Molecular weight: 374.86776
- Additional notes: Using Panc-1 as a model system, it has been demonstrated that CRT0066101: ⢠Reduced bromodeoxyuridine incorporation ⢠Increased apoptosis ⢠Blocked neurotensin-induced PKD1/2 activation ⢠Reduced neurotensin-induced, PKD-mediated Hsp27 phosphorylation ⢠Attenuated PKD1-mediated NF-κB activation ⢠Abrogated the expression of NF-κB-dependent proliferative and pro-survival proteins Molecular Weight: 374.86776 (HCl salt) 338.40712 (free base) g/mol
Handling
- Purity: 374.86776 g/mol
- Shipping conditions: Dry Ice
Target Details
- Primary target: Protein Kinase D (PKD)
- Ic50: IC50 1, 2 and 2.5 nM for PKD1, PKD3 and PKD2 respectively
Application Details
- Application: In Panc-1 subcutaneous xenograft model, orally administration of CRT0066101 at the dosage of 80 mg/kg/d for 24 days significantly suppressed pancreatic cancer growth. Moreover, when CRT0066101 reached its peak concentration (12 Îźmol/L) in tumor model, the expression of activated PKD1/2 in the treated tumor explants was substantially decreased. It was concluded that CRT0066101 given orally at 80 mg/kg/d for 21 days in Panc-1 orthotropic model suppressed tumor growth potently in vivo. Clinical...
Related Tools
- Related tools: Protein Kinase D inhibitor CRT5 (CRT0066051) Small Molecule (Tool Compound)
References
- Harikumar et al. 2010. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1136-1146.PMID: 20442301 Ochi et al. 2011. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 226: 1074-1081. PMID: 20857418 Yuang et al. 2012. Frontiers in Physiology. 3:60. PMID: 22470346 Yang et al. 2013. PNAS (vol 10:6-2312-17). PMID: 23345428 Berhnart et al. 2013. Experimental Cell Research (vol319)-2037-2048. PMID: 23562655 Wei et al. 2014. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. PMID: 24634417 Ryvkin et al. 2015. J Biol Chem. 290(17):11199-208. PMID: 25802335.