Cat. #151267
Anti-BLM [BFL 103]
Cat. #: 151267
Sub-type: Primary antibody
Unit size: 100 ug
Availability: 3-4 weeks
Target: Bloom's Syndrome Protein (BLM)
Class: Monoclonal
Application: WB ; ELISA ; IHC ; IF ; WB
Reactivity: Human
Host: Mouse
£300.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Helen Turley
Institute: University of Oxford
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
- Name: Anti-BLM [BFL 103]
- Clone: BFL 103
- Tool sub type: Primary antibody
- Class: Monoclonal
- Conjugation: Unconjugated
- Strain: Balb/c
- Reactivity: Human
- Host: Mouse
- Application: WB ; ELISA ; IHC ; IF ; WB
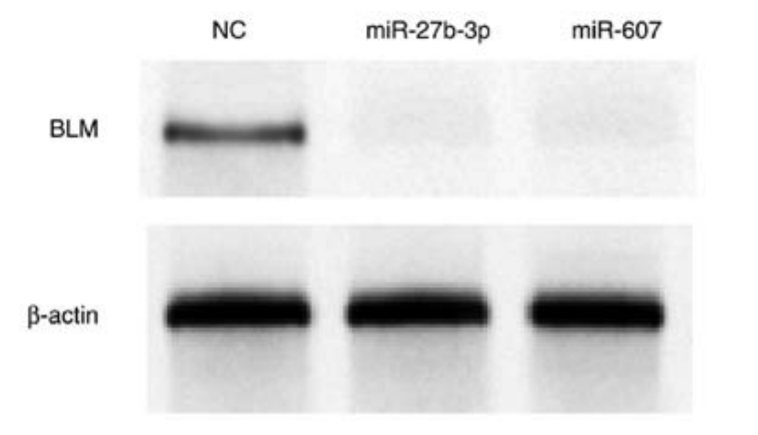
- Description: BLM is the product of the Blooms syndrome gene and belongs to the RecQ family of DNA helicases. BLM is associated with an increase in the incidence of many types of cancer at an early age.
- Immunogen: Recombinant Full Length Bloom's Protein
- Isotype: IgG1
- Myeloma used: P3/NS1/1-Ag4.1
- Recommended controls: Tonsil/thymus
Target Details
- Target: Bloom's Syndrome Protein (BLM)
- Tissue cell line specificity: Tonsil/thymus
- Target background: BLM is the product of the Blooms syndrome gene and belongs to the RecQ family of DNA helicases. BLM is associated with an increase in the incidence of many types of cancer at an early age.
Applications
- Application: WB ; ELISA ; IHC ; IF ; WB
Handling
- Format: Liquid
- Concentration: 0.9 mg/ml
- Unit size: 100 ug
- Storage buffer: PBS with 0.02% azide
- Storage conditions: -15° C to -25° C
- Shipping conditions: Shipping at 4° C
References
- Chen et al. 2019. Mol Med Rep. 19(6):4819-4831. PMID: 30957187.
- Zhu et al. 2008. J Biol Chem. 283(43):29405-15. PMID: 18708356.
- Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) binding determines substrate recognition and paralog-selective SUMO modification.
- Turley et al. 2001. Br J Cancer. 85(2):261-5. PMID: 11461087.
- The distribution and expression of the Bloom's syndrome gene product in normal and neoplastic human cells.
- Wu et al. 2000. J Biol Chem. 275(13):9636-44. PMID: 10734115.
- The Bloom's syndrome gene product interacts with topoisomerase III.